Growing a business requires strategic planning and execution, and two key elements that play a major role in this process are marketing and promotion.
While these terms are often used interchangeably, they are fundamentally different.
- Marketing refers to the broader strategy of understanding customer needs and creating value. This concept extends to building long-term relationships to drive growth.
- Promotion is a specific part of marketing that focuses on increasing visibility, creating awareness, and making people to take immediate action, like sales or sign-ups.
To fully understand their roles, we will:
- Define marketing and promotion.
- Explore their key features, advantages, and disadvantages.
- Highlight the exact differences in a detailed comparison table.
By the end of this blog, you’ll have a clear, structured understanding of how marketing and promotion differ and why both are essential for business success.
What is Marketing?
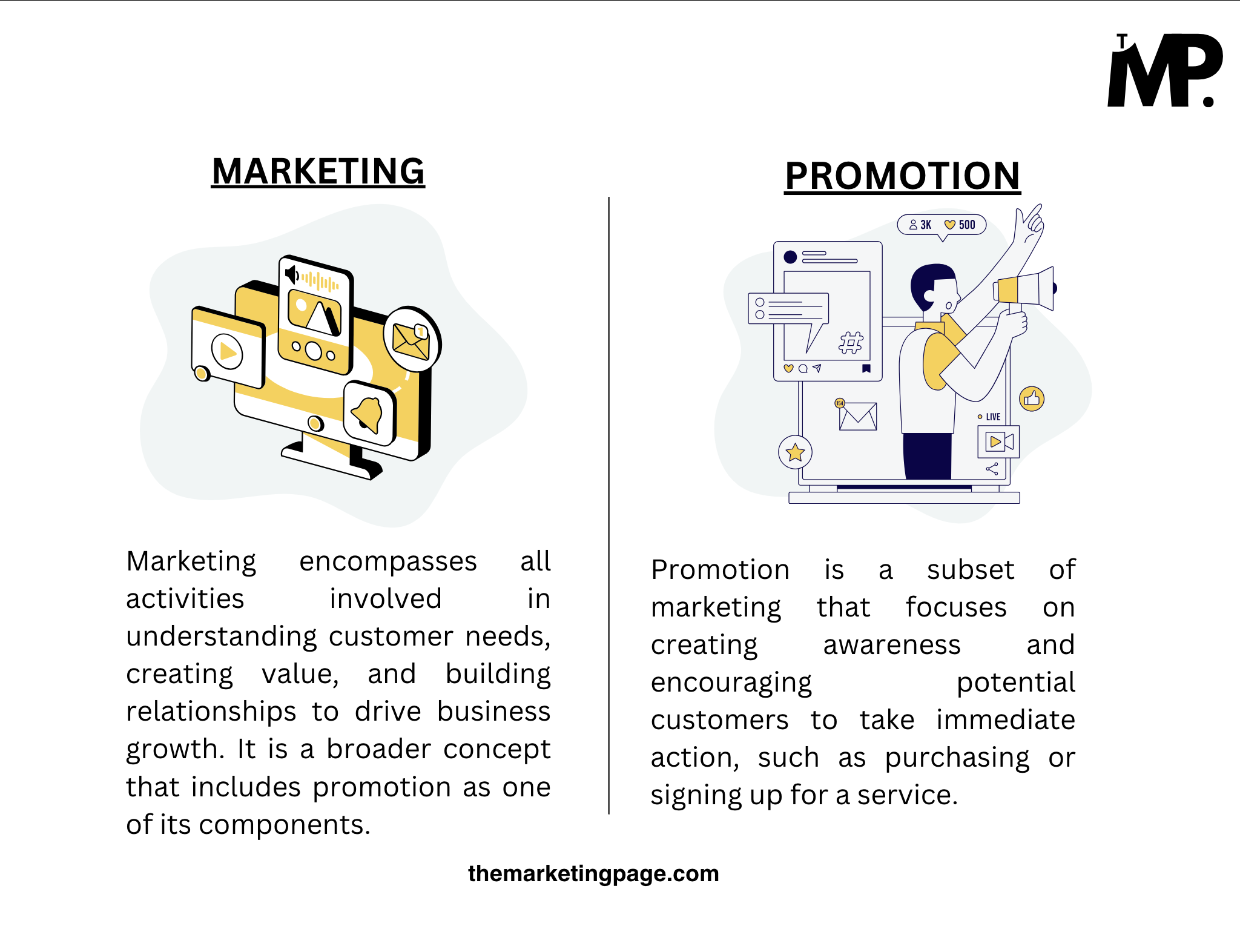
Marketing encompasses all activities involved in understanding customer needs, creating value, and building relationships to drive business growth. It is a broader concept that includes promotion as one of its components.
Key features of marketing
- Focuses on understanding and addressing customer needs.
- Includes market research, product development, branding, pricing, and distribution.
- Builds sustainable relationships with customers.
- Uses digital, traditional, and experiential channels to reach audiences.
- Relies on data and insights to optimize strategies.
Advantages of marketing
- Builds recognition and trust among customers.
- Engages and retains customers through consistent value.
- Converts customer interest into sales.
- Encourages businesses to evolve based on market trends.
- Establishes a framework for business growth.
Disadvantages of marketing
- Requires significant investment in research, campaigns, and tools.
- Needs consistent effort and long-term planning.
- Involves coordinating multiple teams and resources.
- Strategies can be imitated by competitors.
- Results may vary depending on execution and market conditions.
Examples of marketing
- Content marketing: Blog posts, white papers, and case studies.
- Social media marketing: Campaigns on platforms like Instagram and LinkedIn.
- Search engine marketing (SEM): Google Ads and SEO.
- Product marketing: Launching new features or products with targeted messaging.
- Event marketing: Sponsoring industry conferences or hosting webinars.
What is Promotion?
Promotion is a subset of marketing that focuses on creating awareness and encouraging potential customers to take immediate action, such as purchasing or signing up for a service.
Key features of promotion
- Designed to trigger immediate responses.
- Emphasizes achieving quick results.
- Uses discounts, offers, and contests to attract attention.
- Communicates a clear, persuasive value proposition.
- Tracks effectiveness through KPIs like conversions and sales.
Advantages of promotion
- Drives immediate purchases or sign-ups.
- Captures attention with compelling offers.
- Puts brands or products in the spotlight.
- Attracts first-time users with introductory deals.
- Helps move unsold stock.
Disadvantages of promotion
- Benefits are temporary and fade after the campaign ends.
- Frequent promotions can undermine brand value.
- Can strain budgets due to heavy discounts or ad spend.
- Overuse may diminish overall marketing effectiveness.
- May not reach broader or long-term customers.
Examples of promotion
- Seasonal sales like Black Friday or Cyber Monday.
- Contests or free product offers on platforms.
- Limited-time offers sent to subscribers.
- TV, radio, and online ads targeting specific audiences.
- Partnering with events to showcase products.
Key differences between marketing and promotion
The following table provides a detailed comparison of marketing and promotion.
| Aspect | Marketing | Promotion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broader strategy for customer engagement and business growth. | Subset of marketing focused on driving immediate action. |
| Scope | Includes research, branding, distribution, and promotion. | Focuses solely on creating awareness and encouraging quick sales. |
| Timeframe | Long-term, aiming for sustained growth and loyalty. | Short-term, targeting immediate results. |
| Focus | Customer relationships and value creation. | Specific offers or campaigns. |
| Goal | Build brand, engage customers, and drive growth. | Increase visibility and drive quick actions. |
| Tools Used | Market research, content, analytics, and branding tools. | Ads, discounts, giveaways, and event sponsorships. |
| Impact Duration | Long-lasting when executed well. | Temporary; fades after campaign ends. |
| Budget | Often requires larger, more sustained budgets. | Typically requires a smaller, campaign-specific budget. |
| Measurement | Analyzes broad metrics like customer lifetime value. | Tracks KPIs like sales and engagement during campaigns. |
| Dependency | Operates independently but includes promotion as a component. | Relies on broader marketing strategies for context. |
Conclusion: Why Marketing and Promotion Are Essential for Business Success
A business needs these strategies to not only build long-term relationships with customers but also drive immediate actions that lead to conversions.
Marketing and promotion are indispensable.
While marketing builds the foundation for long-term growth, promotion drives immediate results.
Understanding how to effectively integrate both strategies is key.
All you need to understand here is;
- 4Ps of marketing
- Product: Ensure your product meets customer needs and expectations.
- Price: Set a pricing strategy that resonates with your target audience while remaining competitive.
- Place: Identify the best channels to distribute your product effectively.
- Promotion: Strategize how to raise awareness and encourage action through advertising, offers, and events.
- Long-term strategy vs. Short-term goals
- Marketing: Focus on building relationships and brand loyalty for sustained growth.
- Promotion: Drive immediate action through limited-time offers, discounts, and campaigns that capture attention and generate conversions.
- Promotion Mix
- Use a combination of advertising, sales promotions, contests, sponsorships, and events to engage your target audience.
- Experiment with different tactics and measure their effectiveness (e.g., through KPIs like sales or sign-ups).
Businesses can create a well-rounded strategy that not only drives immediate sales but also sets the stage for sustained growth
1 Comment