Businesses are constantly seeking effective ways to attract, engage, and convert potential customers.
Two foundational concepts that play a crucial role in this process are the sales funnel and the marketing funnel.
Although both terms refer to the journey a customer takes before making a purchase, they serve distinct purposes and are designed to address different stages of the customer lifecycle.
What is sales funnel?
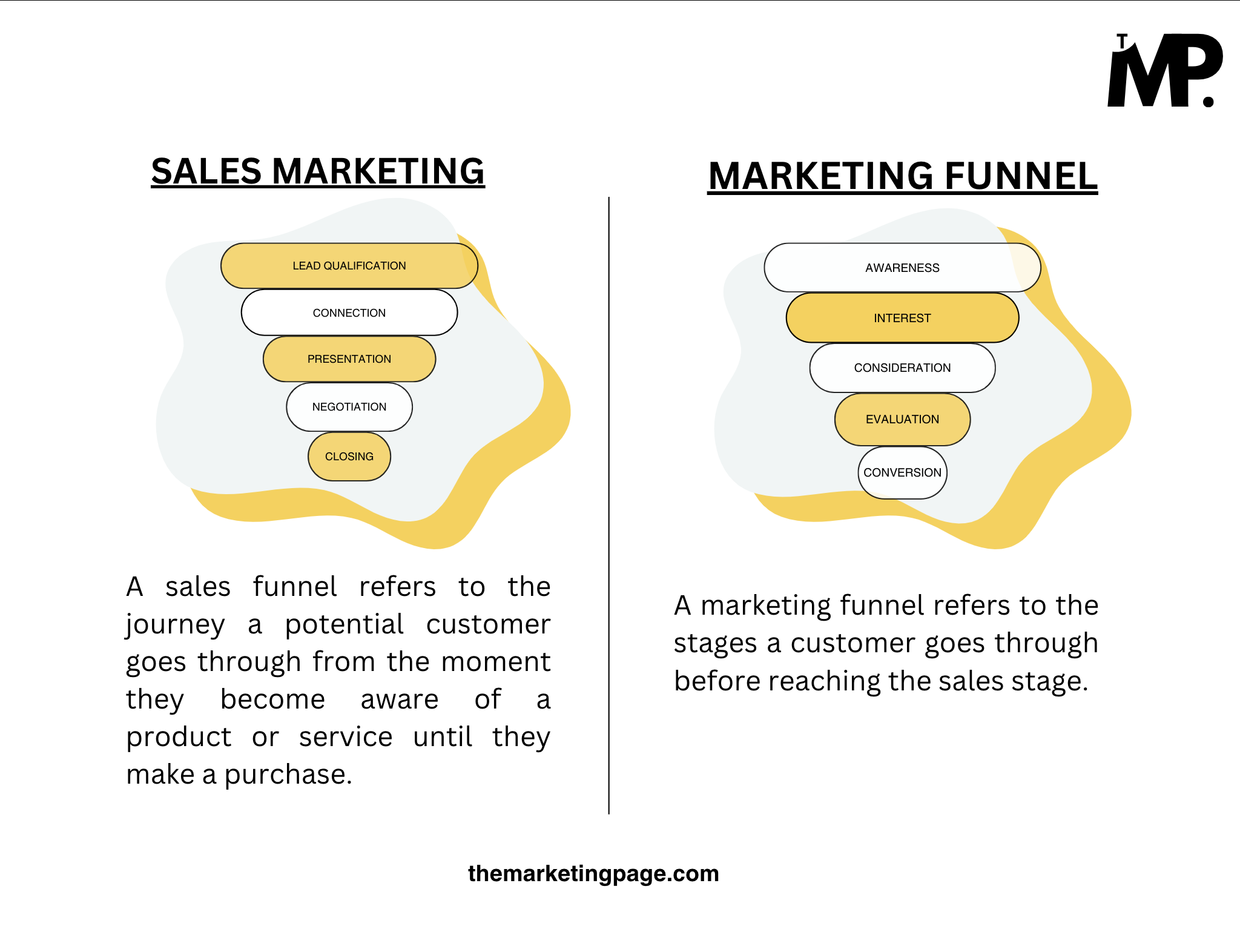
A sales funnel refers to the journey a potential customer goes through from the moment they become aware of a product or service until they make a purchase.
The sales funnel is closely tied to the closing of a sale. The main purpose of this funnel is to nurture leads into conversions. It’s typically a more direct, transaction-oriented approach that focuses on guiding prospects towards making a buying decision.
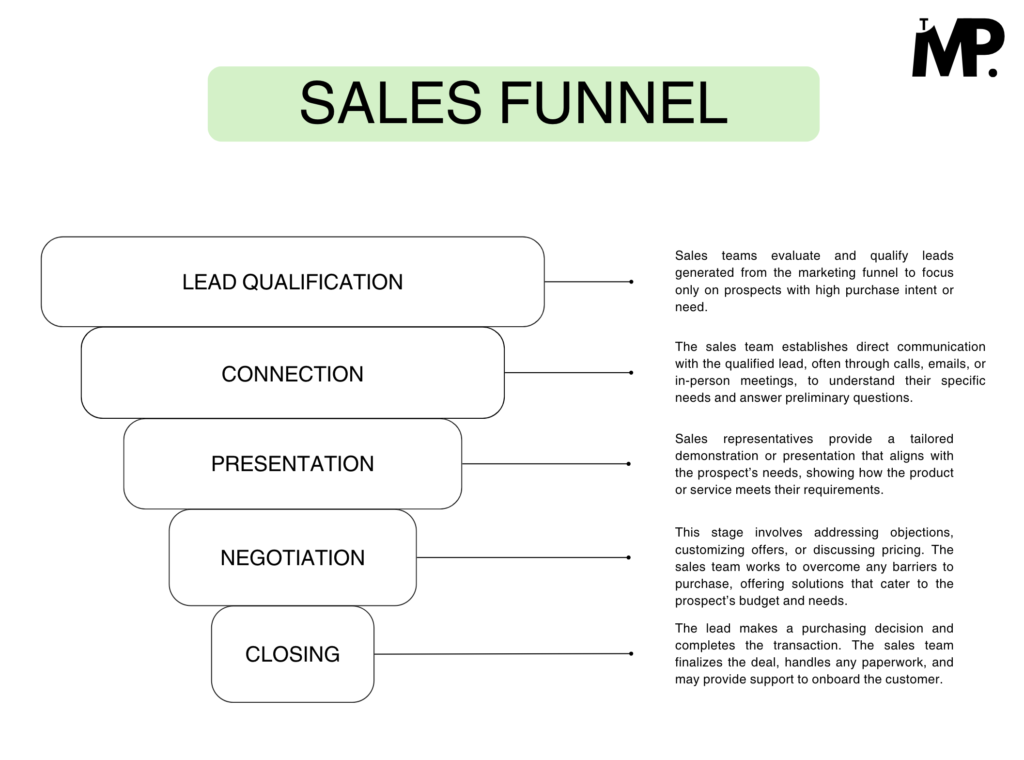
Stages in sales funnel
- Lead Qualification – Sales team identifies and focuses on leads with high purchase potential.
- Connection – Sales initiates direct contact to understand the lead’s specific needs.
- Presentation – A tailored product demonstration highlights the solution’s relevance to the lead.
- Negotiation – Sales addresses objections and customizes offers to overcome purchase barriers.
- Closing – The lead completes the purchase, finalizing the sale.
Key characteristics of the sales funnel
- The sales funnel is designed to convert leads into customers.
- This funnel is typically shorter than the marketing funnel, as it’s focused on the final stages of the customer journey.
- It involves direct interactions with leads, such as sales calls, product demos, and negotiations.
- This funnel assumes that leads are already aware of the brand and interested in the product.
Advantages of the sales funnel
- It helps to clearly define sales goals and ensure that every step in the process is aimed at securing a purchase.
- Since this funnel focuses on individuals who are already interested, it allows for tailored and personalized sales approaches.
- Sales teams can focus on leads that are most likely to convert, streamlining their efforts.
Disadvantages of the sales funnel
- A sales funnel requires consistent follow-up and engagement to ensure leads don’t fall off.
- It does not address earlier stages of the customer journey, such as awareness or education.
- The sales funnel often relies heavily on the performance of the sales team to convert leads.
Example of the Sales Funnel
Imagine a SaaS company that provides project management tools. A potential lead signs up for a free trial after engaging with the brand’s content. Once the lead is on the trial, a sales representative follows up with personalized messages, offering a demo and incentives to purchase the full product. Once the prospect buys the full product, they move out of the sales funnel.
What is a marketing funnel?
A marketing funnel refers to the stages a customer goes through before reaching the sales stage.
It is a broader approach focused on attracting and nurturing leads through content and engagement, usually long before they’re ready to make a purchase.
The marketing funnel’s primary aim is to build awareness and interest, which eventually leads to a handoff to the sales team.
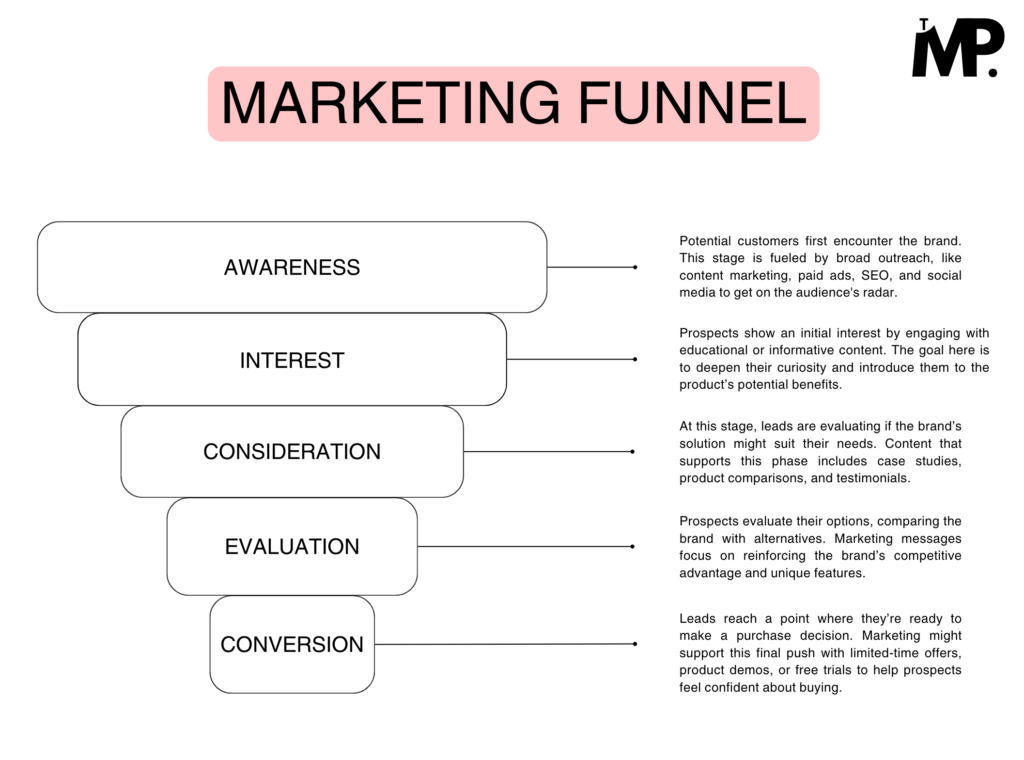
Stages in marketing funnel
- Awareness – Potential customers discover the brand through broad outreach methods.
- Interest – Leads show curiosity by engaging with informative content about the brand.
- Consideration – Prospects evaluate whether the product aligns with their needs.
- Intent – Leads express strong interest through specific actions like sign-ups or webinar attendance.
- Conversion – The lead decides to purchase, becoming a customer.
Key characteristics of the marketing funnel
- The marketing funnel is about generating awareness and educating potential customers.
- It is typically longer and more focused on building trust over time.
- Marketing teams focus on creating content, social media engagement, and building relationships.
- It targets a larger, less defined group of people at the awareness and interest stages.
Advantages of the marketing funnel
- Helps to create lasting customer relationships by educating and engaging prospects.
- It plays a crucial role in increasing brand recognition and credibility.
- It helps to qualify leads before they enter the sales funnel, ensuring the sales team focuses on the right prospects.
Disadvantages of the marketing funnel
- Because the focus is on nurturing, the results from the marketing funnel might take longer to realize.
- Ongoing content creation, social media engagement, and other marketing efforts require significant resources.
- It doesn’t directly lead to conversions but rather works to prepare leads for the sales team.
Example of the Marketing Funnel
Consider a fitness brand that runs paid ads and produces educational blog posts on healthy living and fitness tips. Through these efforts, they generate interest and capture leads via email signups for free ebooks or newsletters. As these leads engage further with the brand’s content, they move closer to making a purchase, eventually passing to the sales funnel when they’re ready to buy.
Key Differences Between Sales Funnel and Marketing Funnel
Here’s a detailed table comparing the Sales Funnel and the Marketing Funnel side by side:
| Aspect | Sales Funnel | Marketing Funnel |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Convert leads into customers | Generate awareness and nurture leads |
| Focus | Closing sales and conversions | Engaging potential customers and building interest |
| Length | Shorter, focused on the final steps of the process | Longer, designed to move prospects from awareness to consideration |
| Key Players | Sales team | Marketing team |
| Target Audience | Qualified leads who are close to making a purchase | A broader audience, typically unaware or in early interest stages |
| Lead Stage | Late-stage (decision and action) | Early to mid-stage (awareness, interest, consideration) |
| Type of Content | Product demos, case studies, testimonials, offers | Blog posts, social media content, educational videos |
| Lead Handling | Direct interaction (calls, demos, meetings) | Indirect interaction (email campaigns, ads, content) |
| Conversion Tactics | Push for purchase, special offers, urgency | Educate, build trust, create interest |
| Metrics | Sales conversion rate, deal size, customer lifetime value | Engagement rate, click-through rate, lead generation |
| Time to Results | Fast (immediate results after closing a deal) | Slow (requires time to nurture and qualify leads) |
Tips to get the most out of these funnels
1. Recognize the Roles of Each Funnel
Understanding both the sales and marketing funnels is essential for any business looking to turn leads into loyal customers.
- The marketing funnel focuses on building brand awareness and nurturing leads. It attracts potential customers and prepares them for the next steps.
- The sales funnel takes over when leads are ready for personalized interactions that guide them toward making a purchase.
2. Align Both Funnels for Seamless Lead Flow
By aligning both funnels, you create a smooth transition from marketing to sales, ensuring leads receive consistent support at every stage. This approach helps to:
- Build trust with potential customers
- Make the buying process feel cohesive and supportive
3. Maximize Your Strategy for Better Results
To get the most from your sales and marketing efforts, follow these steps:
- Use targeted marketing content to attract and educate prospects.
- Gradually guide them through the awareness and interest stages until they show intent.
- When a lead is ready, have your sales team step in with tailored presentations and follow-ups that address specific needs.
4. Create a Comprehensive Customer Journey
By using both funnels in sync, you establish a strategy that not only attracts leads but also converts and retains customers. This combined approach leads to:
- Higher conversion rates
- Stronger customer relationships
- Improved overall business growth
Turns prospects into satisfied, long-term customers.
2 Comments