Ever wondered why some brands feel like they were made just for you?
Think about Netflix recommending a show that perfectly matches your mood. Or Nike’s “Nike By You” service, letting you design sneakers that reflect your personality and performance needs.
These companies don’t just sell products—they solve problems and make you feel like you matter.
And that’s exactly what the marketing concept is all about.
It’s not about pushing products. It’s about understanding what you need and delivering it better than anyone else.
Curious to know why this approach is a game-changer for businesses today? Let’s break it down.
What is the Marketing Concept?
The marketing concept is a business strategy that revolves around identifying and satisfying the needs and wants of customers.
Instead of pushing products or services, companies first ask, What do our customers really want? and then design their offerings to solve those needs.
86% of buyers are willing to pay more for a better customer experience (PwC). That stat alone speaks volumes about the power of the marketing concept.
Imagine you’re shopping for a sofa. Instead of settling for a generic design that doesn’t quite fit your space or style, you discover a company that takes a different approach:
- You choose the size. Perfect for that cozy corner in your living room.
- You select the color and fabric. Whether it’s a bold red or soft beige, it matches your aesthetic.
- You add storage options. Ideal for keeping your living room clutter-free.
This company isn’t just selling furniture—it’s solving your specific problem: limited space and a desire for personalization.
The Marketing Concept Flow Diagram
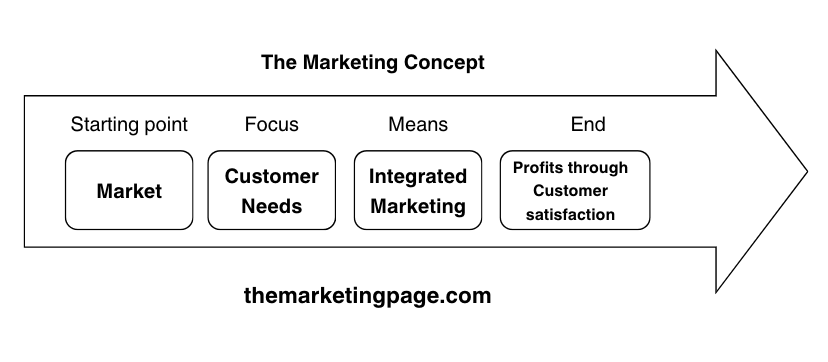
This flow demonstrates how the marketing concept works in a customer-centered approach. The arrow shows a progression from understanding the market and identifying customer needs to integrating marketing efforts, ensuring customer satisfaction, and ultimately achieving profits. It is described below as;
- Market (Starting Point)
- The process begins by identifying and understanding the market—the specific group of customers or audience the company intends to target.
- This means researching potential customers, their preferences, behavior, and needs.
- Customer Needs & Wants
- The next step is to identify customer needs and wants.
- Instead of focusing on what the company can make, this stage involves focusing on what customers actually want or need.
- Companies shift their focus from simply selling to meeting customer demand.
- Integrated Marketing
- Here, the company integrates all aspects of marketing—product design, pricing, distribution, and promotion—to ensure they align with customer needs and provide value.
- This step involves coordinating marketing efforts across different functions within the company to deliver a consistent message and customer experience.
- Profits Through Customer Satisfaction
- The final step is achieving profits by satisfying customer needs.
- Instead of focusing solely on sales volume, success is defined by customer satisfaction, which leads to repeat business and long-term profitability.
Four Core Principles of the Marketing Concept (Explained)
To better understand how the marketing concept works, let’s break it into four core principles:
1. Start with Understanding Your Target Audience
You can’t sell to everyone.
Businesses need to identify their ideal customer base—the people whose needs align with their products or services. This involves thorough research into customer demographics, preferences, and pain points.
Example: A company making baby products focuses on new parents aged 25–40 who value safety and convenience.
2. Focus on Solving Real Problems
The marketing concept isn’t about showing off what you can do; it’s about listening to customers’ needs and finding solutions.
Businesses often conduct surveys, focus groups, or interviews to understand what matters most to their audience.
Example: Ride-sharing apps like Uber and Lyft solve a major problem: the hassle of finding quick and affordable transportation.
3. Integrate Teams to Deliver Value
Marketing isn’t just the responsibility of the marketing department.
It’s a team effort that requires coordination across sales, production, logistics, and customer service. A seamless experience for the customer is only possible when everyone works toward the same goal.
Example: Companies like Starbucks rely on collaboration between their marketing and customer experience teams to offer personalized rewards programs.
4. Aim for Profitability by Creating Happy Customers
Satisfied customers lead to long-term profitability. A business that invests in customer satisfaction often sees repeat purchases, referrals, and better market reputation.
Studies show that 65% of a company’s revenue comes from repeat customers, making loyalty a key driver of success.
Advantages of the Marketing Concept
When businesses embrace the marketing concept, they unlock several benefits:
- By putting customers first, businesses create experiences that leave people feeling valued.
- Companies that solve customer problems are more likely to earn positive reviews and word-of-mouth referrals.
- Happy customers stick around, reducing the cost of acquiring new ones.
- A customer-first approach helps businesses stand out in competitive markets.
- Satisfied customers tend to spend more and are willing to pay for premium experiences.
Disadvantages of the Marketing Concept
While the marketing concept is powerful, it’s not without challenges:
- Understanding customer needs and designing tailored solutions takes time.
- Surveys, data analysis, and customer feedback tools require significant investment.
- The entire team must work together, which can be hard to achieve in larger organizations.
- Misunderstanding customer needs can lead to wasted resources and failed products.
- Businesses relying heavily on current trends may struggle to adapt if preferences change suddenly.
Examples of The Marketing Concepts
Here are some real-world examples of brands that use the marketing concept effectively:
1. Amazon’s “Working Backwards” Approach
Amazon’s strategy is simple, yet powerful: they start with the customer and work backwards. Here’s how it works:
- Before launching anything, Amazon creates an imaginary press release.
- This press release focuses on how the product or service will benefit the customer.
- From there, they design everything around these customer needs.
The result? Every new product or service is guaranteed to meet a clear customer need, making Amazon the ultimate go-to for convenience and personalization.
By putting customers at the core of their innovation, Amazon has become a master at delivering exactly what people want—fast, efficient, and tailored to individual preferences
2. IKEA’s Customer-Centered Solutions
IKEA isn’t just about selling furniture—it’s about solving real problems. Here’s how they do it:
- Affordable, flat-packed designs make transportation and assembly easy for customers.
- In-store experiences like childcare facilities make shopping more convenient for families.
- The focus on functionality and value ensures that every product fits seamlessly into customers’ lifestyles.
It’s this customer-first approach that keeps shoppers coming back for more.
3. Netflix’s Data-Driven Personalization
Netflix isn’t just guessing what you want to watch—they’re using data to know exactly what you love. Here’s how they do it:
- Advanced data insights track user behavior to predict preferences.
- Personalized recommendations suggest shows you’re likely to enjoy based on what you’ve watched.
- Original content production is driven by audience interests, ensuring shows are made for your taste.
This data-driven strategy keeps users engaged and loyal, making Netflix the go-to streaming platform for personalized entertainment. It’s all about ensuring you get the best content, every time you log in.
4. Starbucks’ Customer Loyalty Programs
Starbucks knows how to keep you coming back. Here’s how their loyalty programs work:
- Custom Orders: Their app lets you tailor every drink to your exact preferences.
- Rewards: Collect points with every purchase for free drinks and discounts.
- Special Perks: Get treats like free birthday drinks, making customers feel appreciated.
By focusing on personalization and rewards, Starbucks turns regular customers into loyal brand advocates, creating a strong emotional connection with every cup.
Conclusion: Key Lessons for Marketers
The marketing concept is more than a business strategy—it’s a mindset. For marketers and businesses to succeed in today’s competitive landscape, they must embrace these key lessons:
- Always start with the customer.
- Create value, not just products.
- Work as a team
- Focus on long-term loyalty
- Adapt to change
When businesses focus on delivering value, they not only win customers—they create relationships that last a lifetime.

1 Comment