The interplay between products (that they offer) and markets (in which they serve) is crucial for any business aiming to achieve sustainable growth. I believe that this combination can significantly impact their success.
Businesses often turn to strategic frameworks like BCG Matrix, Product Life cycle, SWOT Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces and a lot more that provide clear direction in the market landscape.
Also Read: The Five Marketing Concepts
One such framework is the Product Market Expansion Grid. We also call it Ansoff Matrix.
In this article, I’ll tell you about;
What is Product-Market Expansion Grid?
The Product-Market Expansion Grid, also known as Ansoff Matrix, was introduced by Igor Ansoff in 1957 as a strategic tool.
He developed this framework to provide organizations with a structured approach to expanding their market presence and product offerings.
The Product-Market Expansion Grid is a strategic tool that helps businesses identify opportunities for growth by analyzing their current products and markts while also assessing the associated risks of different growth strategies.
Igor Ansoff believed that the product market holds great importance for businesses as it serves as the foundation for their growth and success.
The triplet of specifications – the product-market scope, the growth vector, and the competitive advantage – describes the firm’s product market path in the external environment.
IGOR ANDOFF ALTER, P. 110 – CORPORATE STRATEGY, 1965
Introduction to the Ansoff Matrix:
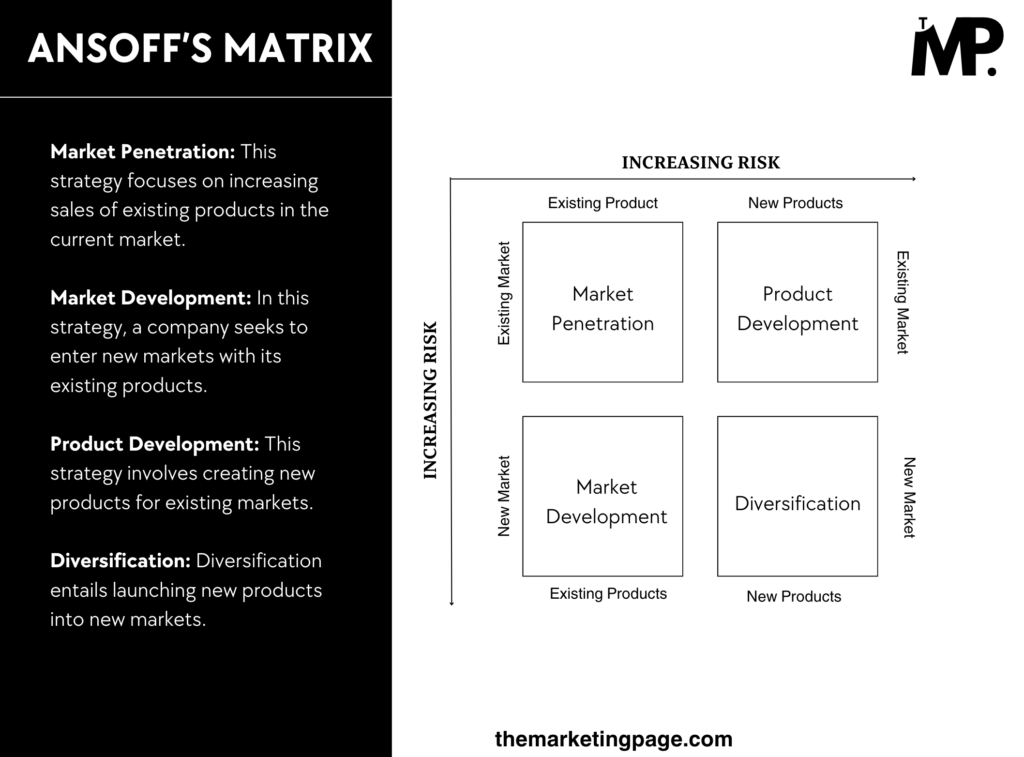
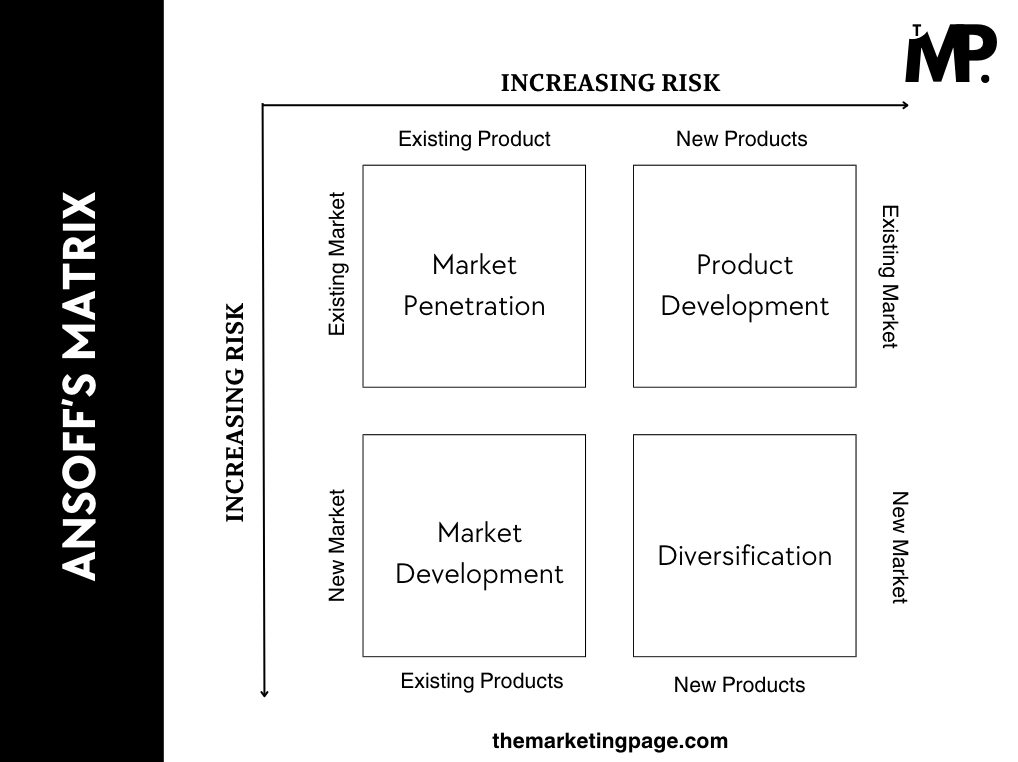
The grid operates on a two-dimensional matrix, with one axis representing products (existing and new) and the other representing markets (existing and new).
The four main strategies for growth considered in the grid are;
- Market penetration
- Market development
- Product development
- Diversification
Two key factors of the Product Market Expansion Grid
The Product-Market Expansion Grid revolves around two essential factors:
- Product
- Market
These factors are represented on the two axes of the grid. Eacg factor plays a crucial role in guiding businesses toward effective growth strategies.
1. Product (Vertical Axis)
On the vertical axis, we have Products. These can be categorized as either existing or new. It is important to take note of the distinction between new and existing because it helps businesses assess their current portfolio and identify opportunities.
- Existing products: These are the products that a company currently offers. Understanding how to increase sales or market share of existing products is crucial for market penetration strategies.
- New products: These include innovations or variations of products that a company plans to introduce. This factor is significant for product development strategies. This is where businesses aim to create new offerings to meet evolving customer needs.
Focusing on the product aspect allows companies to evaluate their strengths and weaknesses in product development. This helps in meeting market demands and the ability to innovate also improves.
2. Markets (Horizontal Axis)
On the horizontal axis, we have Markets. These can be categorized as either existing or new. This classification helps businesses determine their market expansion strategies based on their current market preence.
- Existing markets: These are the current markets where a company operates. Understanding these markets help businesses formulate market penetration strategies. Existing markets focus on targeting increased sales and deeper market share.
- New markets: These are untapped or under-served markets where a company seeks to expand its reach. Exploring new markets is essential for market development strategies. New markets allow companies to diversify their customer base.
Businesses can make informed decisions by analyzing the market dynamics.
Four quadrants of Ansoff Matrix
Now, let’s discuss each of the four quadrants of the Product Market Expansion Grid. Each strategy has its unique characteristics and risks.
1. Market Penetration
Market penetration focuses on increasing sales of existing products in existing markets. Essentially, it aims to capture a larger share of the current market.
This strategy often involves tactics like aggressive marketing, pricing adjustments, or improving customer service.
Risk Level: Generally, market penetration is considered less risky compared to other strategies since the company is already familiar with the market and product.
It can be achieved by;
- Increasing promotional efforts i.e. advertising and marketing campaigns
- Attracting existing customers for repeated purchases through loyalty programs.
- Adjust prices to attract more customers from competitiors.
2. Market Development
Market development involves introducing existing products into new markets. This could mean targeting different geographic areas or new customer segments.
Companies may enter new regions or demographics, potentially leveraging their current products.
Risk Level: This strategy carries moderate risk, as it involves entering unfamiliar markets, which may have different consumer behaviors and preferences.
It can be achieved by;
- Opening stores or services in new locations.
- Targeting new demographics (age groups, income levels, or lifestyles, etc.)
3. Product Development
Product development focuses on creating new products for existing markets. This strategy is about innovation and addressing customer needs with fresh offerings.
It may include product line extensions or entirely new products that cater to the current customer base.
Risk Level: This strategy can be moderately risky, depending on how well the new products align with customer expectations.
It can be achieved by;
- Investing in R&D to create new products that meet emerging customer needs.
- Improving existing products based on customer feedback and trends.
4. Diversification
Diversification involves launching new products into new markets. This strategy is often seen as a way to reduce risk by spreading investment across various areas.
Companies may explore completely different markets or sectors that are unrelated to their current offerings.
Risk Level: Diversification carries the highest risk since it involves both new products and new markets, requiring a deeper understanding of unfamiliar territory.
It can be achieved by;
- Buying businesses in new industries to gain immediate access to different markets.
- Collaborating with companies that have expertise in new markets or product lines.
| Strategy | Risk Level | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Market Penetration | Low | Involves increasing sales of existing products in existing markets. Lower risk due to familiarity with both the product and market. |
| Market Development | Moderate | Involves entering new markets with existing products. Risk arises from unfamiliar market conditions and competition. |
| Product Development | Moderate to High | Involves creating new products for existing markets. Risk comes from product acceptance, development costs, and market fit. |
| Diversification | High | Involves introducing new products into new markets. High risk due to unknown products, markets, and competition. |
This table provides a quick overview of the risk levels associated with each strategy, helping businesses assess potential challenges as they plan their growth.
Advantages of product market expansion grid
The key advantages of using the product market expansion grid are;
- The Ansoff matrix is easy to understand.
- It helps businesses plan growth strategies clearly.
- It helps identify potential risks associated with different growth strategies.
- The matrix ensures that market plans are aligned with overall business goals.
- It guides businesses in allocating resources to the promising growth opportunities.
- The framework promotes a deeper understanding of both current and new markets.
- It aids in finding unique opportunities for differentiation.
- It is versatile and applicable across various industries.
The Ansoff Matrix and marketing
It’s a valuable marketing tool for companies looking to assess their growth strategies effectively.
Here’s how this matrix can be utilized in marketing:
Strategic planning to set clear goals
The Ansoff Matrix provides a structured framework for businesses to align their growth strategies with clear objectives.
It simplifies complex growth decisions by categorizing them into four strategies—market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification.
This clarity ensures that businesses not only understand where they are but also chart actionable steps to where they want to go.
The matrix can adapt to different industries and scales, whether a startup or an established enterprise. Moreover, it helps allocate resources effectively by focusing efforts on strategies with higher potential ROI.
Example: A smartphone company looking to increase revenue might use market development by expanding sales to regions like Southeast Asia. Instead of spreading itself thin, the matrix guides the company to focus on tailoring its approach to the new market, such as localized marketing campaigns or region-specific features.
Risk assessment identifies potential challenges
Understanding risks is at the core of the Ansoff Matrix, as every strategy carries varying degrees of uncertainty.
By categorizing strategies by risk levels, businesses can evaluate potential pitfalls and create plans to mitigate them.
- Low-Risk Options: Market penetration and market development usually carry fewer risks since they rely on either current products or familiar markets.
- High-Risk Moves: Diversification poses the greatest challenge, requiring new product creation and entry into unknown markets.
- Informed Decision-Making: Risk assessment within the matrix allows businesses to weigh potential challenges before committing resources.
A beverage company entering the health food industry faces higher risks due to unfamiliar customers and competitors. By understanding these risks, they could mitigate failure by partnering with experts or starting with a smaller product line.
Tip: Diversification should always start small—test the waters with a pilot product before diving into full-scale launches.
Marketing mix adjustments
The Ansoff Matrix requires businesses to evaluate and adjust their marketing mix—product, price, place, and promotion—based on the selected growth strategy.
For instance, a product development strategy may necessitate increased investment in research and development (R&D) to innovate or enhance products, as well as a robust mechanism for gathering and analyzing customer feedback.
djustments in pricing strategies might be essential to reflect new value propositions, while promotional efforts may need to shift focus to highlight new features or benefits.
Competitive analysis evaluates market position
The Ansoff Matrix also helps businesses to study their competitors’ strategies through the same lens. This allows for;
- Identifying Gaps: Companies can find unaddressed areas in the market to target.
- Find Opportunity for Differentiation: Helps businesses stand out by offering unique features or approaches.
- Understanding Competitor Weaknesses: Analyzing where competitors fall short enables strategic positioning.
Example: If competitors focus on market penetration, like increasing their market share in existing regions, a company might choose product development instead—introducing innovative features their rivals lack.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Does the growth matrix works?
The effectiveness of the Product Market Expansion Grid depends on various factors, including market conditions, competition, and internal capabilities. Companies that use this grid effectively can:
- Adapt and evolve
- Identify growth opportunities
- Make informed decisions
Q2: Which Product Market Combination has the greatest potential?
Determining which product-market combination offers the most significant growth potential involves several factors. Here are a few considerations:
- Diversification: While riskier, this strategy can be the most rewarding if executed well. Companies that can successfully identify new markets and products that align with their core competencies can experience explosive growth.
- Market Penetration: This is often the safest bet, especially for established brands. Focusing on increasing market share with existing products can lead to steady growth.
- Market Development: When companies have strong products but are limited by market reach, exploring new markets can yield substantial benefits.
- Product Development: For businesses in rapidly changing industries, innovating and developing new products can provide a competitive edge and keep the brand relevant.
Q3: What if my company is startup?
Startups often benefit from focusing on market penetration or product development. This approach allows them to build a customer base and refine their offerings.
Q4: How do I decide which strategy in Ansoff Matrix to pursue?
Assess your current market position, resources, and customer insights. Consider conducting market research to understand potential opportunities.
Q5: What are some common pitfalls in these strategies?
Common pitfalls in Ansoff Matrix strategies are;
- Market penetration pitfalls
- Overestimating customer loyalty can lead to stangation.
- Neglecting competition actions may result in lost market share.
- Inadequate market research can casue ineffective marketing strategies.
- Market development pitfalls
- Insufficient localization may alienate potential customers.
- Ignoring regulatory barriers can lead to costly setbacks.
- Overlooking market demand can waste resources and damage reputation.
- Product Development Pitfalls:
- Underestimating R&D costs can hinder innovation.
- Overcomplicating products may confuse customers.
- Neglecting feedback loops can result in offerings that miss the mark.
- Diversification Pitfalls:
- Lack of expertise in unfamiliar industries can lead to strategic missteps.
- Diluting brand identity may confuse customers about core values.
- Overextending resources can weaken overall business performance.
Conclusion
The Product Market Expansion Grid serves as a valuable guide for businesses seeking growth opportunities. By understanding its components—market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification—companies can make informed decisions that align with their objectives and market conditions.
Rather than just guessing which direction to take, the grid provides a clear map of options on how to approach new markets and products.
Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned professional, grasping the nuances of this framework can significantly enhance your strategic planning and execution, paving the way for sustainable growth in a competitive landscape.
Leave a Comment