The BCG Matrix serves as a powerful tool to evaluate NVIDIA’s diverse product portfolio based on market growth and share.
With its emphasis on market dynamics, the BCG Matrix provides a clear view of NVIDIA’s strategic priorities, highlighting areas of growth and stability.
Overview of NVIDIA
NVIDIA, founded in 1993, is a global leader in semiconductors, specializing in GPUs, AI hardware, and system-on-chip units for diverse markets. Led by CEO Jensen Huang and Chief Scientist Bill Dally, NVIDIA operates in over 80 countries with 29,600 employees (FY2024).
In FY2024, NVIDIA reported $60.92 billion in revenue and $29.76 billion in net income.
Its GeForce GPUs dominate the gaming market, while its professional GPUs are used in fields like AI, automotive, and scientific research. Competitors include AMD, Intel, and AI-focused firms like Cerebras. Strategic initiatives focus on advancing AI, data centers, autonomous vehicles, and edge computing solutions.
BCG Matrix of NVIDIA
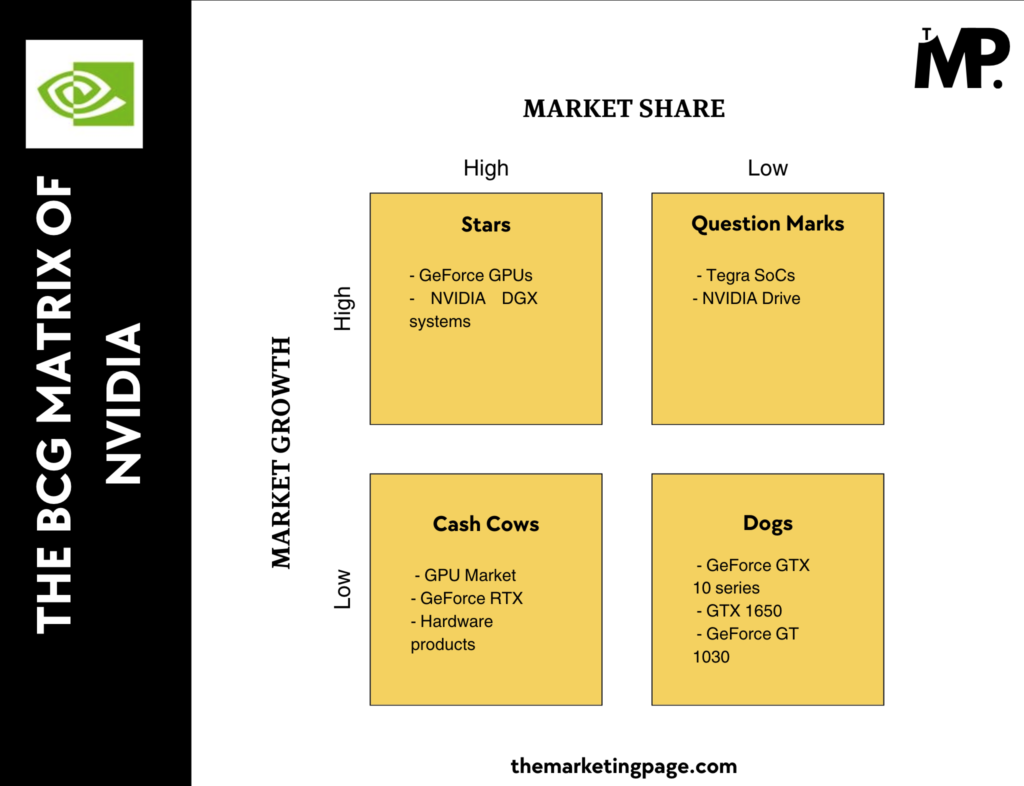
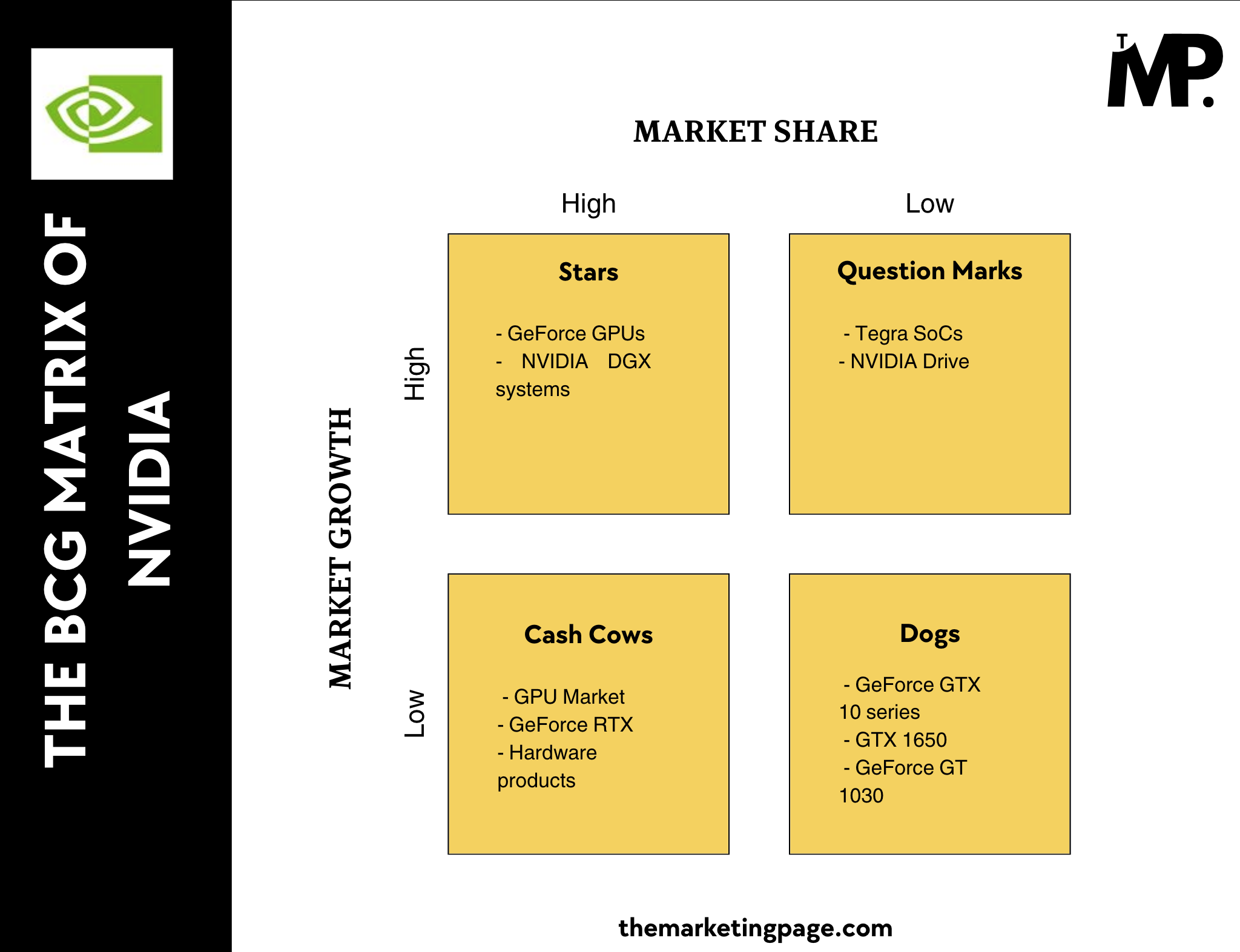
This is the break down NVIDIA’s product portfolio using the BCG Matrix in terms of market share and growth.
Let’s see in depth how BCG Matrix can be a better to way have analysis of facts that can help it in business decisions with market performance for long-term success.
1. Stars (High Market Share, High Market Growth)
Key Products: GeForce GPUs, NVIDIA DGX systems
NVIDIA’s GeForce GPUs and DGX systems are its Stars.
They dominate the market with cutting-edge innovation and thrive in a high-growth sector like gaming, AI, and data science.
GeForce GPUs are at the heart of the booming gaming industry, which is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.9% from 2023-2030. Their widespread adoption among gamers and creators ensures NVIDIA maintains a high market share.
Meanwhile, NVIDIA DGX systems are critical for AI research, powering advancements in machine learning and AI-driven applications, industries expected to surge in the coming years. These products lead both innovation and market expansion.
2. Cash Cows (High Market Share, Low Market Growth)
Key Products: GPU Market, GeForce RTX, hardware products
NVIDIA’s GPU market dominance and GeForce RTX series are clear Cash Cows. These products have a high market share but operate in relatively mature or slower-growing segments.
NVIDIA’s hardware, especially the RTX series, remains a consistent revenue generator thanks to its dominance in the gaming and workstation markets. While growth isn’t as rapid as before, the steady demand for RTX GPUs among gamers, professionals, and creators keeps the cash flowing.
Additionally, NVIDIA’s overall GPU market leadership (over 90% market share in discrete GPUs) ensures a stable revenue stream despite limited market growth.
3. Question Marks (Low Market Share, High Market Growth)
Key Products: Tegra SoCs, NVIDIA Drive
Products like Tegra SoCs and NVIDIA Drive fall under the Question Marks category. These are in high-growth sectors but lack a dominant market share.
Tegra SoCs power NVIDIA’s initiatives in mobile devices and the Nintendo Switch, yet they face stiff competition from rivals like Qualcomm.
Similarly, NVIDIA Drive, which focuses on autonomous vehicle solutions, is positioned in a high-growth market (expected to reach $614.88 billion by 2030 with a CAGR of 24.9% from 2023 to 2030). However, adoption is still slow, and competitors like Intel’s Mobileye pose significant challenges.
The potential is there, but these products need strategic investment to capture more market share.
4. Dogs (Low Market Share, Low Market Growth)
Key Products: GeForce GTX 10 series, GTX 1650, GeForce GT 1030
The GeForce GTX 10 series, GTX 1650, and GT 1030 represent NVIDIA’s Dogs.
These older-generation i.e. GTX 10 series GPUs have minimal technological updates and low demand, leading to a declining market share in a stagnant or shrinking segment.
For example, the GTX 1650, released in 2019, hasn’t seen meaningful updates, while the GT 1030 uses outdated architecture and struggles to maintain relevance.
With NVIDIA’s focus shifting to newer technologies like the RTX series and AI-driven products, these legacy GPUs are no longer competitive. They contribute little to overall revenue and are on their way out.
Conclusion
NVIDIA’s strategy revolves around innovation and market leadership. It can balance its portfolio by;
- Focusing on AI, gaming, and data centers to drive innovation.
- Investing in autonomous vehicles and edge computing for future growth.
- Phasing out outdated products to streamline its portfolio.
- Building ecosystems through software frameworks like CUDA and AI tools.
Note: It’s important to note that this analysis represents a limited snapshot in considered factors (market share and market growth) and time (2024).
Also read, BCG Matrix of Sony [2024]
Leave a Comment